The shoulder is made up of three bones: the scapula (shoulder blade), clavicle (collarbone) and humerus (upper arm bone). Two joints in the shoulder allow our shoulder to move: the acromioclavicular joint, where the highest point of the scapula (acromion) meets the clavicle, and the glenohumeral joint.
The glenohumeral joint is the one most people think of as the shoulder joint. It is formed where a ball (head) at the top of the humerus fits into a shallow cuplike socket (glenoid) in the scapula, allowing a wide range of movement. Because the socket of the shoulder is shallow, the joint relies on surrounding soft tissues to support it and hold the components in place.
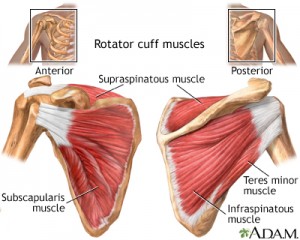
Each muscle of the shoulder assists with specific movements. Keeping the head of the humerus inside the glenoid fossa is the primary function of the rotator cuff muscles. This important group of muscles lies just outside the glenohumeral joint and helps rotate the shoulder in many directions. The rotator cuff muscles include the:
- Supraspinatus which controls the abduction (when lifting sideways the arm)
- Infraspinatus & teres minor muscles (SIT) which control the outward rotation of the arm
- Subscapularis which controls the inward rotation of the arm
Supraspinatus tendinitis is often associated with impingement syndrome. Its causes can be broken down into primary impingement, which is a result of increased subacromial loading, and secondary impingement, which is a result of rotator cuff overload and muscle imbalance. Supraspinatus tendinitis is also a common cause of shoulder pain in athletes, whose sports involve throwing and overhead motions.
The term tendinitis (or tendonitis) is the pathological condition of the tendon inflammation that characterizes the acute phase of the problem. Here, the symptoms are intense within the first 24 hours with severe pain and medication has a dominant role.
When the symptoms have subsided slightly, it is recommended to assess the damage and design the physiotherapy plan for a complete tendon repair.
Manual therapy, Medical Exercise Therapy, Kinetic control, Kinesiotaping, etc have exceptional results.
This post is also available in: Greek